What is HCR silicone?
Heat Cured Rubber is a silicone elastomer formed of straight chains with very high molecular weight. The system will be cured with either an organic peroxide crosslinker, or a platinum catalyst. HCR offers great temperature and aging resistance.
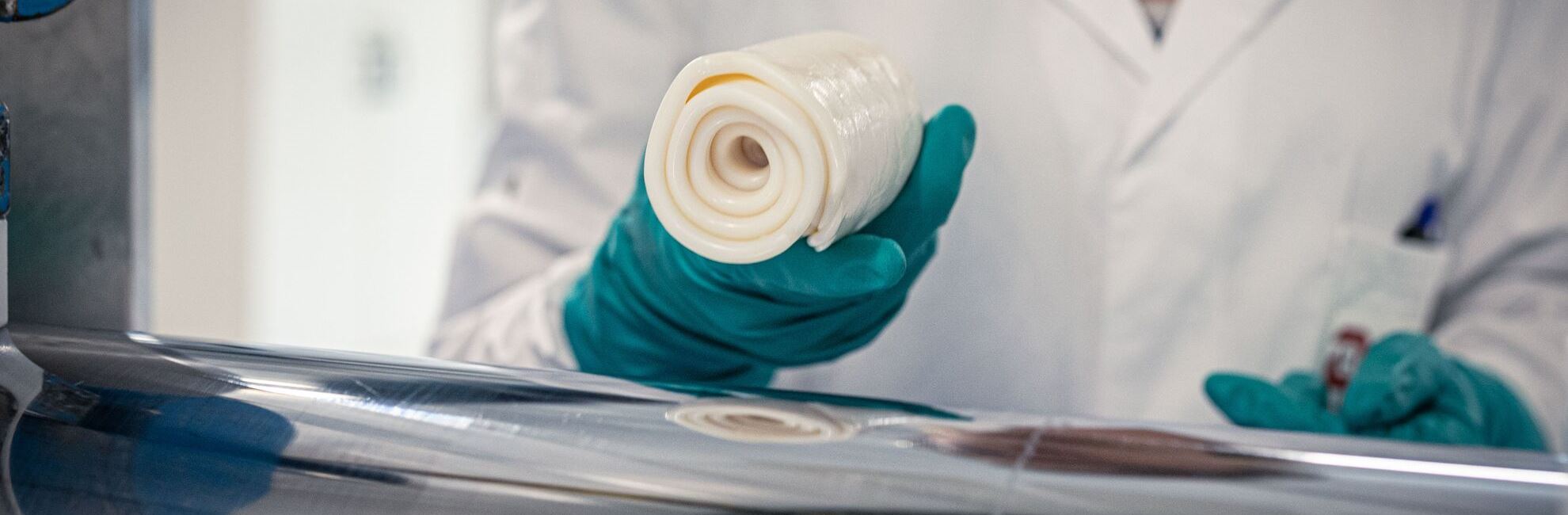
Chemical structure
Heat Cured Rubber elastomers are also known as High Temperature Vulcanizing silicone rubber (HTV). They are made from reactive silicone gums, in other words, straight chains, with very high molecular weight macromolecules containing various reactive groups. The most frequently used gums are either partly phenylated or perfluorinated vinylated gums. Various raw materials are added to give additional properties to the HCR e.g. fumed or precipitated silicas with high specific surface area to improve mechanical properties, heat stabilizers and various other additives such as plasticizers or anti-structuring agents. Cross-linking occurs using organic peroxides in polycondensation systems or platinum catalysts in polyaddition systems.
Silicone Rubber
HCR, together with LSR are also commonly known under the umbrella name of Silicone Rubbers
HCR silicone properties
Heat Cured Rubber elastomers have outstanding properties and are far superior to conventional organic elastomers. They exhibit exceptional mechanical strength at temperature and can be used at temperatures ranging from -50 °C to +300 °C. The aging resistance of these elastomers highlights their fundamental qualities such as the fact that they are chemically inert, their photo-oxidative stability and the absence of residual reactive groups once cured. A wealth of colorings are possible. By using a sufficiently fine silica filler it is even possible to make transparent articles for use in food and paramedical applications. The addition of various additives opens unlimited for customization of HCRs to create solutions to all kind of existing and new applications in Aerospace, Automotive, Healthcare, Oil & Gas, Construction, Electronics. Most recent examples are heat transfer additives for Electrical Vehicles, electrical conductive materials for Power or Consumer Electronics and also antibacterial solutions for Healthcare applications.
Let’s take the example of electric vehicle to understand the benefits of HCR. As we have seen above the technology exhibit resistance to high and low temperatures and they offer flexibility for added properties. Automotive cable manufacturers have therefore been using silicone rubber HCR instead of other polymers (such as TPU/TPE and XLPE) to ensure longer aging time under high temperatures and easy install in the increasingly smaller spaces found in newer generation automobiles. Cables made with HCR can match the needs generated by constant innovation in the Electric Vehicle industry, especially for the connection between the engine and the battery.
HCR’s sustain heat and present fire resistance with low smoke emissions and non-corrosive and non-toxic combustion gasses. They offer reliable insulation and mechanical performance at a low weight.
Revision Sheet
Technology
HCR
Definition
HCR means High Consistency Rubber, or Heat Cured Rubber, main formula (Gum+Silica+Plasticizer+Additives)
General information
Good thermal stability up to 300 ℃; Cold resistance to -50 ℃, some special grade could reach -120 ℃ or above 300 °C; Good electrical properties
Typical properties
- Hardness 30~80 ShA
- Mechanical strength 7~10 MPa
- Elongation 200~800 %
- Tear strength 15~40 N/mm
Curing Mechanism
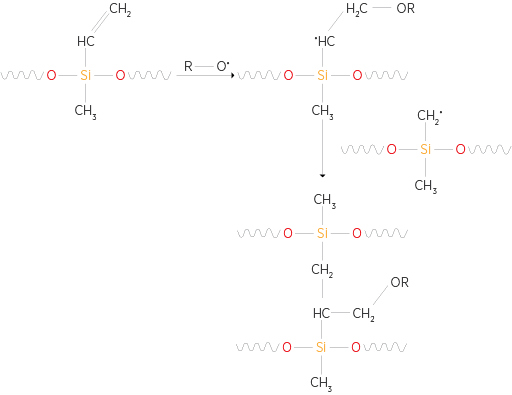
Processability
Kneader mixing to adding color and catalyst on 2-roll mill to filtration
Application/final products
Automotive application (Cables, hoses, gaskets, anti-vibration), Medical devices (tubes, connectors, cables, long term implants), Electrical application (insulators, cables), Kitchenware and consumer applications.
Why use HCR silicones?
Related applications

HCRs outstanding properties are used in many different industrial applications: sealing and piping in fluid circuitry (joints for building construction and aeronautical applications, automotive gaskets, boots and hoses), electrical protection (office equipment safety cables and insulators for electrotechnical applications, spark plug boots, cables and connectors for automotive application), food, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications (tubes, profiled sections).
What are the different processing methods for silicone rubber?
This blog article explores the five silicone rubber processing methods and their advantages, for us in an almost endless number of different applications.
Related products
THE DIFFERENT MANUFACTURING METHODS
Contact us
Take your business to the next level by partnering-up with a global leading material manufacturer.