- Elkem
- Sustainability
- Climate strategy
- Positions and FAQ
- Statements and positions
Statements and positions

Animal testing
Our position
Extensive scientific information is requested under the REACH regulation to ensure legal chemical safety compliance, this leads to mandatory animal testing. Elkem makes every effort to limit animal testing to required and mandatory tests requested by authorities.
We develop, whenever possible, the use of recognized alternative methods like in-vitro testing and grouping strategies allowing read-across to other substances with similar properties or chemical structures. Elkem is actively working within several industry consortia concerning REACH to exchange scientific information and improve best practices within the industry.
Disclosure of substances produced that are covered by relevant international conventions and regulations
We comply with all regulations and are legally obliged to create and supply internationally compliant Product Safety data Sheets which are available on our website through the Product Finder.
Biocarbon
Our position
The Silicon and Ferro-silicon production process uses carbon sources like fossil coal, charcoal and wood chips as reductant agents in the chemical conversion. This releases CO₂ emissions as an inherent part of the process and cannot be avoided with today’s technology.
However, it is possible to replace the fossil coal/carbon with biobased materials – which are viewed as CO₂ neutral due to their biogenic nature.
Our ambition is to increase the raw material based on biocarbon – charcoal and wood chips – by 20% by 2021, and replace 40% of fossil carbon with biobased raw materials by 2030. Our percent target is based on the absolute input of raw materials per year. Meaning that, if our production increases, so must our use of biocarbon materials, to reach our target.
Our long-term ambition is to be carbon neutral by 2050. Technology development on energy consumption and in the production process, introducing more and more raw materials based on biogenic sources and innovation and development within carbon capture and usage/storage (CCU/CCS) will be necessary to reach this ambition.
What is biocarbon?
Biocarbon is any carbon based on biogenic raw material. This can be anything from wood and forest to food waste. For Elkem, the biobased material that we use is based on wood, like trees from forests or plantations. We are also looking into if we can use recycled wood, example from buildings. The quality and pureness of the material is key here.
The biobased carbon goes back into the carbon circle, from a tree back to a tree after use, and therefore is viewed as CO₂ neutral when used in the process industry. By introducing biobased raw material, we can replace the use of fossil coal and therefore also replace our fossil emission with biobased emissions.
Responsible sourcing
It is vital for Elkem that the biocarbon we buy are sustainably sourced and focus on high ethical and environmental standards from our suppliers. The charcoal suppliers are subject to strict controls to ensure raw material from certified, sustainable sources and that working conditions in the production process are acceptable and comply with human rights.
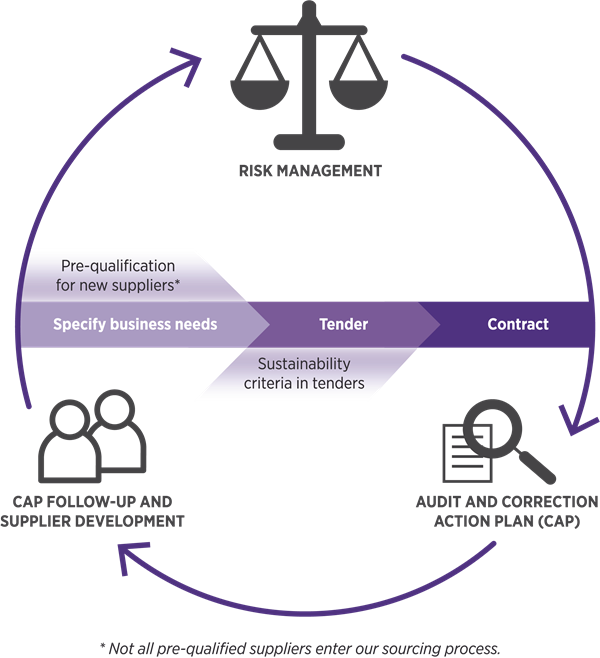
Responsible sourcing is a strategic priority for Elkem. Responsible sourcing means looking at what we procure beyond the more traditional aspects such as cost, quality and delivery time. It means that Elkem is committed to consider ethics, labour rights, social and environmental issues when sourcing products and services across all procurement categories and across all operations.
Bio-diversity
Our position
Elkem is committed to preserving biodiversity and ecosystems around our facilities. Elkem recognises the importance of considering relevant environmental aspects, including consideration of water quality, soil conditions, habitats, vegetation, and the physical stability of landforms and decommissioned structures.
It is vital for Elkem to uphold our responsibility for limiting our environmental impact from our operations and Elkem supports the conservation of biodiversity and promotes sustainable land management practices. To ensure this, Elkem continues to evaluate the risks around existing facilities and has to date not found substantial issues.
Elkem supports the global principles of the UN Convention of Biological Diversity, and is committed to avoid operating in protected areas or areas with importance for biodiversity. Elkem does not have any operations located in or adjacent to protected areas and has not identified any significant impacts on biodiversity, protected habitats or endangered species.
When applicable, Elkem will ensure consultation with local and national authorities, as well as the local community and NGO's on issues regarding biodiversity in order to protect local interests. Elkem will follow the principles of the mitigation hierarchy in order to ensure biodiversity conservation: avoidance, minimisation, rectification and compensation.
Carbon capture and storage
Our position
Carbon capture storage (CCS) and carbon capture and utilisation (CCU) are key to reach the targets defined by the Paris Agreement and for the process industry to become climate neutral. This is also outlined in the Norwegian process industry roadmap (in Norwegian only).
Elkem accords importance to the initiatives to build a Norwegian CCS infrastructure. Establishing a CO₂ storage and transport facility is a prerequisite to develop a market for capturing CO₂.
The Norwegian CCS initiatives are particularly interesting to Elkem, as close to 60% of the company’s scope 1 emissions are from the smelters producing silicon and ferrosilicon in Norway.
Elkem has been part of several R&D and feasibility study projects to assess how CCS and CCU can be connected to Elkem’s smelters, including an R&D project to close the silicon furnace and a carbon capture feasibility study.
Circular economy
Our position
Circular economy is an enabler to our sustainability engagement. Waste management has long been part of our lean management culture and faced with ever more pressing industrial and societal environmental challenges, we have the will, through an ambitious “Circular economy roadmap”, to meet this growing demand from both our customers and other stakeholders
Elkem believes that circular economy includes at least three components:
The first is a technical and industrial component. Thanks to our advanced processes, we know how to minimise our waste or reprocess it. Several plants already have a "zero waste roadmap”.
The second is in connection with our customers and partners. How can we offer them new services and products that are even more respectful of the environment? How can we take their production by-products and give them a second life? These are questions we need to ask ourselves in order to develop new business models and enhance circularity
The third and last, but certainly not the least important component is employee involvement. The engagement of all our employees is essential to create and proliferate this new mindset, whether in our everyday life or in the development of a new product, process or service.
Stop waste, think circular!
Coal tar pitch
Our position
Elkem Carbon is one of the world’s largest manufacturer of Søderberg electrode paste that is used in metal production around the globe. Historically, Søderberg electrode paste has been made of coal tar pitch and coke. The use of coal tar pitch, high temperature, requires authorisation under the European REACH regulation. However, since the use of coal tar pitch in Søderberg electrodes is considered as intermediate, it is exempted from authorisation. Elkem Carbon has been working successfully on the replacement of hazardous pitch with green substitutes and can now offer an increasing range of products free of polycyclic, aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH). This is an important step towards a non-toxic workplace environment, for both Elkem and customers.
Conflict minerals
Our position
Conflict minerals refers to raw materials or minerals that come from a particular part of the world where conflict is occurring and affects the mining and trading of those materials. These conflict minerals are tin, tantalum, tungsten (the “3T’s”) and gold.
Elkem is committed to responsible sourcing of minerals, including 3T, cobalt and gold, using the OECD Guidance, so as not to support any possible conflict with human rights abuses or environmental degradation. Elkem uses chemical compounds made from some of these in small quantities in the silicones production process and has strict sourcing controls to ensure that procurement of these are done in full compliance with applicable European and US regulations. Where EU and US regulations does not apply, we expect that our conflict minerals policy to be followed, both by Elkem and in the supply chain.
See the responsible sourcing of conflict minerals policy for more information
D4/D5/D6
Our position
D4, D5 and D6 are key intermediates for all silicone products. There has been extensive research and discussion the past years to identify and verify possible hazards with these products, but environmental authorities around the world have still not come to a common understanding of the possible environmental effects.
Elkem continues to take all necessary steps to reduce any environmental risk. Elkem’s ambition is to be ahead of both regulatory demands and market and customer expectations. Our work therefore centres around understanding and meeting regulatory restrictions, offer our customers best in class products and reduce the presence of D4, D5 and D6 where possible.
Our target is zero deviation on regulatory compliance regarding the management of D4/D5/D6.
What is D4, D5 and D6?
For silicones, D4 D5 and D6 are used as intermediates in the production process and used to produce downstream silicone polymers for a wide range of silicone based products.
Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4), Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5) Dodecamethylcyclo- hexasiloxane (D6) are cyclosiloxanes, and basic members of the silicone family, serving as the building blocks for many silicones. They are used to create a diverse range of silicone materials (polymers) that provide beneficial characteristics to a wide variety of applications and products, including construction, electronics, engineering, health care and personal care among others.
D4, D5 and D6 are most frequently used as raw materials for polymer manufacturing, meaning that the substance is employed in the manufacturing process, but is only present at very low (trace) levels in the end products.
Our safety work and research on D4/D5/D6
The silicones industry continues to study the safety of cVMS and actively collaborates in research programs with academic experts as well as government scientists around the world. The extensive database of health, safety, and environmental data for D4, D5 and D6 continues to support their safe use in a wide range of markets and product applications.
The silicone industry, including Elkem Silicones, is collaborating actively with the regulatory authorities in the different regions, providing data from environmental monitoring studies and additional health and safety research, including a Global Human Health Risk Assessment based on both potential environmental and product-use exposures.
The available data supports that:
- D4, D5 and D6 do not behave as PBTs in the environment because they do not biomagnify up the food chain and cannot reach concentrations in the environment that might cause harm. Consequently, they should not be regarded or regulated as PBTs.
- D4, D5 and D6 may be transported long distances, but break down in the atmosphere, do not back-deposit, and cannot reach concentrations in the environment that might cause harm. D4 should not be considered as a POP substance.
- D4, D5, and D6 do not pose a risk to human health or the environment.
- D4, D5, and D6 are safe for use in consumer products when those products are used as intended.
The industry will continue to work with regulatory authorities around the world to determine the most appropriate measures to effectively address any potential concerns that may arise. It is also informing the authorities of the many benefits associated with silicones and the socio-economic consequences of disproportionately regulating the substances as PBTs.
Elkem has launched a global technology project to reduce the 3 Ds to <0,1% where possible with a triple ambition of meeting regulatory restrictions, satisfy customer requirements and apply best available manufacturing technology.
Are D4, D5 and D6 safe for the environment and/or human health?
Yes. D4, D5 and D6 are safe for the environment and for human health, when used for their intended purposes.
Large volumes of monitoring data collected by the global silicones industry, academic experts/institutes and governmental regulatory agencies globally, continue to demonstrate that D4, D5 and D6 are not found at, nor are likely to be found at, levels that pose a risk to the environment. Since they are volatile, the majority of D4, D5 and D6 are released to the atmosphere or will evaporate quickly into the atmosphere if released in other media. Once in the atmosphere, D4, D5 and D6 break down due to natural, physical processes.
Observed levels monitored in a wide variety of temperatures and surroundings do not give rise to any concern. The more than 60 years of use have therefore not led to any environmental concern, and based on the observed data the industry does not expect this to change. Multiple lines of evidence show the environmental levels are not increasing even though uses of silicones have considerably grown over years.
In Europe, Elkem Silicones is an active member of the CES – Silicones Europe and support the organisations efforts to clarify regulatory commitments.
Guarantee of origin
Our position
Elkem uses location based methodology when we report our electricity consumption and its associated CO₂ emissions as this makes for consistent reporting for all our plants worldwide. This methodology is consistent with the entire Norwegian process industry sector. We seek to locate our plants in regions with predominantly renewable power production. By using location based methodology, Elkem does not buy guarantees of origin.
Elements of concern
Our position
For the production of Elkem’s silicon products and ferroalloys, natural raw materials are carefully selected in order to meet the product specifications. Natural raw materials, as well as the final products, may contain trace amounts of “elements of concern”, i.e. heavy metals. However, the concentration of such elemental impurities is as low as a few ppm (parts per million) and thus, far below the generic threshold value of 0.1% that would trigger regulatory action. No SVHC’s currently listed on REACH annex XIV, are intentionally added to Elkem’s silicon and ferroalloy products. A number of leaching tests have been carried out on Elkem’s products in order to assess bioavailability of elements of concern. Leaching of critical elements is so low that the products would comply with European regulations for the use in toys (EN 71-3, safety of toys) or in electronic equipment (RoHS directive), and even meet the recommendations of the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment Germany for fillers in polymers with food contact (BfR LII).
Lobby position
Elkem seeks to obtain a satisfactory regulatory framework for all its operations. In Europe, this entails a sufficient allocation of CO₂ allowances as well as compensation for CO₂ expenses in the power price. For Norway specifically, Elkem seeks a favourable outcome of the ongoing revision of the industrial grid tariff scheme, as well as to limit the number of interconnectors between Norway and other countries as well as to work in favour of a Norwegian power system that ensures a stable and sufficiently low power price.
Membership organisations overview
Elkem operates in many countries worldwide. Sites and plants have memberships both locally, regionally and nationally that are based on the local site or plants network and organisation. These can be based on business, education/academia and innovation/R&D. The list below shows the most material memberships, from Elkem corporate position in Norway and Europe.
|
Elkem ASA |
Organsiation |
Who they are |
Reach |
2020 fee and sponsorships (NOK = exl. VAT) |
2021 fee and sponsorships (NOK = exl. VAT) |
|
Signatory |
UN Global Compact |
UN initiative to implement universal sustainability principles and for businesses to support the UN goals |
Global |
65 777 NOK |
66 272 NOK |
|
Member |
Biceps |
Network of shippers joining forces to accelerate the transition in the global shipping sector towards more sustainability |
Global |
2000 euro |
19 977 NOK (2000 euro) |
|
Member |
Eurometaux European Association |
An umbrella association representing the interests of the combined non-ferrous metals industry towards EU policy makers |
Europe |
513 156 NOK |
509 219 NOK |
|
Member |
Norsk Industri /NHO |
Employer organisation + sub-organisation for industry |
Norway |
2,75 mill NOK |
2,44 mill NOK |
|
Member / Board member |
Forum for miljø-teknologi |
Working to ensure that environmental technologies are realised |
Norway |
150 000 NOK |
150 000 NOK |
|
Member |
Norwegian Chinese Chamber of commerce |
Provide a professional and social forum for those wishing to participate in the Norwegian-Chinese business and cultural communities, thus promoting business opportunities between the two countries. |
Norway (China) |
13 500 NOK |
13 500 NOK |
|
Member / Board member |
Norsk Biokullnettverk |
Gather all actors in the biocarbon value chain in Norway |
Norway |
45 000 NOK |
26 250 NOK (only six month due in 2021) |
|
Member / |
Eyde cluster |
Cluster in South, for process industry and its stakeholders |
Regional NOR |
210 000 NOK |
201 250 NOK |
|
Member / Board member |
Arctic Cluster Team |
Cluster in North, for industry actors |
Regional NOR |
75 000 NOK |
|
|
Member |
Green industry cluster / Powered by Telemark |
Network organisation for technology and industry organisations in Telemark and Vestfold |
Regional NOR |
12 500 NOK | 29 900 NOK |
| Member |
European Carbon and Graphite Association |
ECGA is the Carbon and Graphite Industry's authoritative voice on all Europe related issues |
Europe |
14 000 euro |
|
|
Member |
Global Silicones Council | The Global Silicones Council (GSC) is a not-for-profit, international organisation representing companies that produce and sell silicone products around the world. |
Global |
350 000 dollar |
|
|
Member |
EuroAlliages | Organisation representing the European silicon and ferro-alloys industry towards EU policy makers. |
Europe |
|
1,63 mill NOK |
Product stewardship
Our position
Elkem works to ensure safe handling, use and disposal of our products. Product stewardship is the responsible and proactive management of health, safety and environmental aspects of a product throughout its lifecycle. It includes fully understanding potential hazards with our products and giving clear information on safe use and handling through safety data sheets and other information to customers and partners.
See our product stewardship policy here
Elkem is committed to comply with international regulatory requirements and provides safety data sheets (SDS) for all products in accordance with UN Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). In all markets where Elkem’s products are promoted, the products must meet specific requirements and comply with certain technical, regulatory, health and environmental standards.
Our customers have their own health, safety and environmental requirements for their products. The majority of Elkem’s SDS are available for download on our website. The SDS for some selected products are only available on request, due to the protection of confidential business information.
Safe transportation
Potential hazards in connection with the transportation, handling and storage of all of Elkem’s raw materials and products are fully analysed, and measures to ensure this can be done safely are documented and made available to logistics supplier and customers. The main risks include loss of containment leading to the possibility of fire or toxic release from raw materials and products under transportation. Logistics suppliers that handle hazardous goods for Elkem are closely screened and required to have all applicable certifications for vehicles and drivers. In Europe there is also close cooperation between different chemical producers with agreements to give assistance to each other in case of emergency situations with the transportation of hazardous goods.
Product stewardship for chemicals
Proactive management of use of chemicals and the protection of the environment and the human heath are fundamental pre-requisites for conducting our business and securing our licence to operate. Compliance with chemical product regulations include product registrations, product authorisations, safety data sheets and product labels. There are also industry specific regulations that Elkem complies with, for example for products that are in contact with food and water (packaging) or health care (band aid/wound care).
In addition to comply with all chemical production regulations, the Silicones division is a signatory of the Responsible Care Global Charter of the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA). Product stewardship is the key pillar of the Responsible Care programme and by participating, we have committed us to manage chemicals safely throughout the life cycle. This includes both proactively identifying and managing chemical risks and concerns throughout our operations, and replace substances in the portfolio that pose unacceptable risk to human health, safety and environment.
Site closure
Elkem’s chemical and smelting plants and mines are expected to remain in full operation in the foreseeable future. Site closures are very rare to the company. However, Elkem is committed to ensure good practice by incorporate closure panning in the early stages of site’s life cycle.
Any closure activities will be integrated into our business plans and will include a short-, medium- and long-term planning process for the possible closure. Elkem is committed to rehabilitate and minimise the negative impacts on the environment and landscape. This includes impacts on water, soil, habitats, vegetation and the physical condition and stability of landforms.
Elkem will communicate with and include relevant stakeholders in the process of site closure. This includes relevant industries, communities and governments. Through stakeholder engagement, Elkem will plan for the social transition of the relevant communities in order to mitigate negative impacts for the workforce and the community.
For more information, please see our site closure policy.
Substance of very high concern (SVHC)
A vital part of the European REACH regulation (Regulation (EC) 1907/2006 on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) is the identification and authorisation of substances of very high concern (SVHC). The European Chemicals Agency ECHA regularly updates its SVHC candidate list for authorisation.
In accordance with REACH article 31, it is the manufacturer’s obligation to inform its customers about the presence of SVHC it the respective products when they exceed the generic concentration limit of 0.1 %. Those SVHC substances must also be disclosed in the safety data sheet.
Elkem complies with the provisions of REACH related to SVHC, i.e. communication in the supply chain through safety data sheets.
Elkem regularly monitors its product portfolio for SVHC substances that are subject to existing or future regulatory requirements or that are associated with particular concerns. We review our management plans regularly defining the specific risks associated with each identified SVHC substance. We review all possible options to mitigate identified risks including possible substitution where possible, phasing-out any substance posing an unacceptable risk to human health and/or the environment or limiting the exposure of the SVHC substance if substitution is not deemed possible.
Elkem has three main product areas where SVHC occur:
- In carbon products: high temperature coal tar pitch (CAS no. 65996-93-2) is used as an intermediate in the production of Söderberg electrode paste.
- In silicones: D4, D5 and D6 are key intermediates in the production of silicones-based polymers. In addition some other and essential SVHC substances are used under strict conditions in a limited number of products
- In silicon products and ferroalloys: those are made from natural raw materials such as quartz, coal, and iron oxide that often contain trace amounts of heavy metals. Cadmium and lead are listed as SVHC but their concentration in Elkem’s products are far below the generic threshold limit value of 0.1 % w/w and do not trigger regulatory action.
The only exception is Söderberg electrode paste from Elkem Carbon, which is used as an intermediate and which is as such exempted from authorisation requirements. Elkem Carbon is successfully working on substitution.
